by Harmony Kwiker | Blog
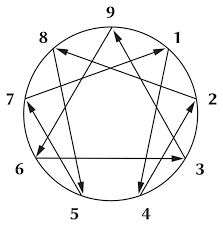
The Enneagram is a tool for awakening, self-discovery, personal growth, and understanding human relationships. It’s a model of the human psyche that describes nine interconnected personality types, each with unique strengths, weaknesses, motivations, and fears. It can be an extremely useful tool to help identify patterns of thinking, feeling, and behavior.
Early on in my career, I leaned heavily on the Enneagram for my self-development, as well as to help me understand my client’s inner map. However, I was noticing that this tool, like many others, was being misused by the general population. Instead of a tool for awakening, it became a tool to reinforce hyper-identification. Knowing our Enneagram type can serve as a clear mirror of understanding that ultimately supports differentiation from the personality.
When we identify with a map or place a map onto a client, we reduce them down to a type instead getting to know their unique inner territory. Because of this, I stopped using the Enneagram with clients and I decide not to bring it into my classrooms with student therapists. Nonetheless, it still greatly informs my ability to understand my clients’ inner map. I find that knowing the stress and heal patterns is helpful in my understanding, but in this article I am going to focus on a new take of the use of the Enneagram: Using the Enneagram to identify polarities for a gestalt two-chair experiment.
In case you’re new to the Enneagram, the 9 types are as follows:
Type 1: The Reformer: Their motivation is to be principled and idealistic. They are perfectionistic, striving to improve themselves and those around them. They are tend to not trust their body, and their mind can get hooked into thoughts of anger and resentment of those who don’t meet their standards. Their habitual patterns are being critical, conscientious, principled, and often rigid in their thinking and actions. The basic fear of the 1 is of being bad or wrong, defective, or evil. Fixation: Resentment. Body Type, motivated by anger.
Type 2: The Helper: Their motivation is to be compassionate and generous. They are caring and desire to be needed and loved. Their habitual patterns are people-pleasing, caring, possessive, and can become manipulative or self-sacrificing. Their basic fear is being unloved, insignificant, or unworthy of care and attention. Fixation: Pride. Heart type, motivated by shame.
Type 3: The Achiever: Driven, ambitious, and success-oriented, focused on achieving their goals and gaining recognition. Their habitual patterns include being driven, adaptable, image-conscious, and can become competitive or superficial in their pursuit of success. Their basic fear is of being a failure, inadequate, or unworthy of achievement. Fixation: Vanity and Deceit. Heart Type, motivated by shame.
Type 4: The Individualist: Romantic, expressive, and introspective, often feeling misunderstood and seeking authenticity. Their habitual patterns include being expressive, dramatic, self-absorbed, and can become moody or introspective. Their basic fear is being ordinary, insignificant, or losing their sense of self. Fixation: Envy. Heart type, motivated by shame.
Type 5: The Investigator: Knowledge-seeking, analytical, and independent, valuing their intellectual pursuits and self-sufficiency. Their habitual patterns are being perceptive, analytical, secretive, and can become isolated or detached. Their basic fear being helpless, incompetent, or feeling overwhelmed by the world. Fixation: Stinginess/Avarice. Mind type, motivated by fear.
Type 6: The Loyalist: Dependable, loyal, and cautious, seeking security and stability in their lives and beliefs. Their habitual patterns include being anxious, responsible, suspicious, and can become cautious or even paranoid. Their basic fear is being insecure, helpless, or losing control of their environment. Fixation: Insecurity/Cowardice. Mind type motivated by fear.
Type 7: The Enthusiast: Energetic, optimistic, and adventurous, seeking joy, variety, and new experiences. Their habitual patterns are being spontaneous, versatile, acquisitive, and can become scattered or impulsive. Their basic fear Being deprived of pleasure, experiencing pain, or being confined to a boring life. Fixation: Planning. Mind type, motivated by fear.
Type 8: The Challenger: Strong, assertive, and protective, motivated by a desire to control their environment and defend their values. Their habitual patterns being self-confident, decisive, willful, and can become confrontational or domineering. Their basic fear of being weak, helpless, or vulnerable to injustice. Fixation: Vengeance. Body type, motivated by anger.
Type 9: The Peacemaker: Accepting, trusting, and stable, seeking harmony and avoiding conflict. Their habitual patterns are being self-forgetful, procrastination, and conflict avoidant. Their basic fear is being in conflict, losing connection with others, or experiencing discord. Fixation: Laziness. Body type motivated by anger.
In the above description, the fixations and basic fears of each type are bolded. This is to highlight the polarity that these types find themselves trapped in. In a recent article (click here to read) I shared about how to identify a polarity in gestalt therapy. What i didn’t write about was the way the Enneagram can support our ability to clearly see the two opposing qualities that cause a client’s inner conflict. Below, you will see the way each type’s fixations create an inner conflict with their basic fear.
Type 1: Resentment is polarized by the fear of being bad or wrong, defective, or evil.
Type 2: Pride is polarized by the fear of being unlovable, insignificant, or unworthy of care and attention.
Type 3: Vanity and deceit is polarized fear is of being a failure or inadequate.
Type 4: Envy is polarized by the fear of being ordinary or insignificant or losing their sense of self.
Type 5: Stinginess/Avarice is polarized by the fear of being helpless, incompetent, or feeling overwhelmed by the world.
Type 6: Insecurity/Cowardice is polarized by the fear of being insecure, helpless, or losing control of their environment.
Type 7: Planning is polarized by the fear of being deprived of pleasure, experiencing pain, or being confined to a boring life.
Type 8: Vengeance is polarized by the fear of being weak, helpless, or vulnerable to injustice.
Type 9: Laziness is polarized by the fear of being in conflict, losing connection with others, or experiencing discord.
To learn about our trainings, visit us at https://awakenedtherapist.com/holistic-therapy-trainings/
To listen to our podcast, visit us at https://awakenedtherapist.com/awakened-therapist-podcast/
References: Riso, D. and Hudson, R. (1999). The Wisdom of the Enneagram: The Complete Guide to Psychological and Spiritual Growth for the Nine Personality Types. Bantam; 11th edition.